What Data Is Disorganized And Not Easily Read
Reading time: 14 minutes
Co-ordinate to IBM, the global volume of data was predicted to attain 35 zettabytes in 2020. Since it increases daily, data scientists wait that the number volition hit 175 zettabytes in 2025. Pic this: 35ZB holds approximately 1 trillion hours' worth of movies. It will take 115 million years to watch all those movies. Those are some impressive figures, aren't they? Well, in that location's something even more impressive about the global information sphere. The prevailing office of data, which is lxxx percent or so, is unstructured. This means structured data only has about 20 percent of all generated information.
In this article, you'll go a closer look at structured vs unstructured data. Let's see what the deviation between the two is and why you should know it in the first place. As well, we will aid you lot understand how to handle each information type and what software tools are bachelor for each purpose.
Structured vs unstructured data in a nutshell
Data exists in a plethora of dissimilar forms and sizes, but most of information technology can be presented as structured information and unstructured data.
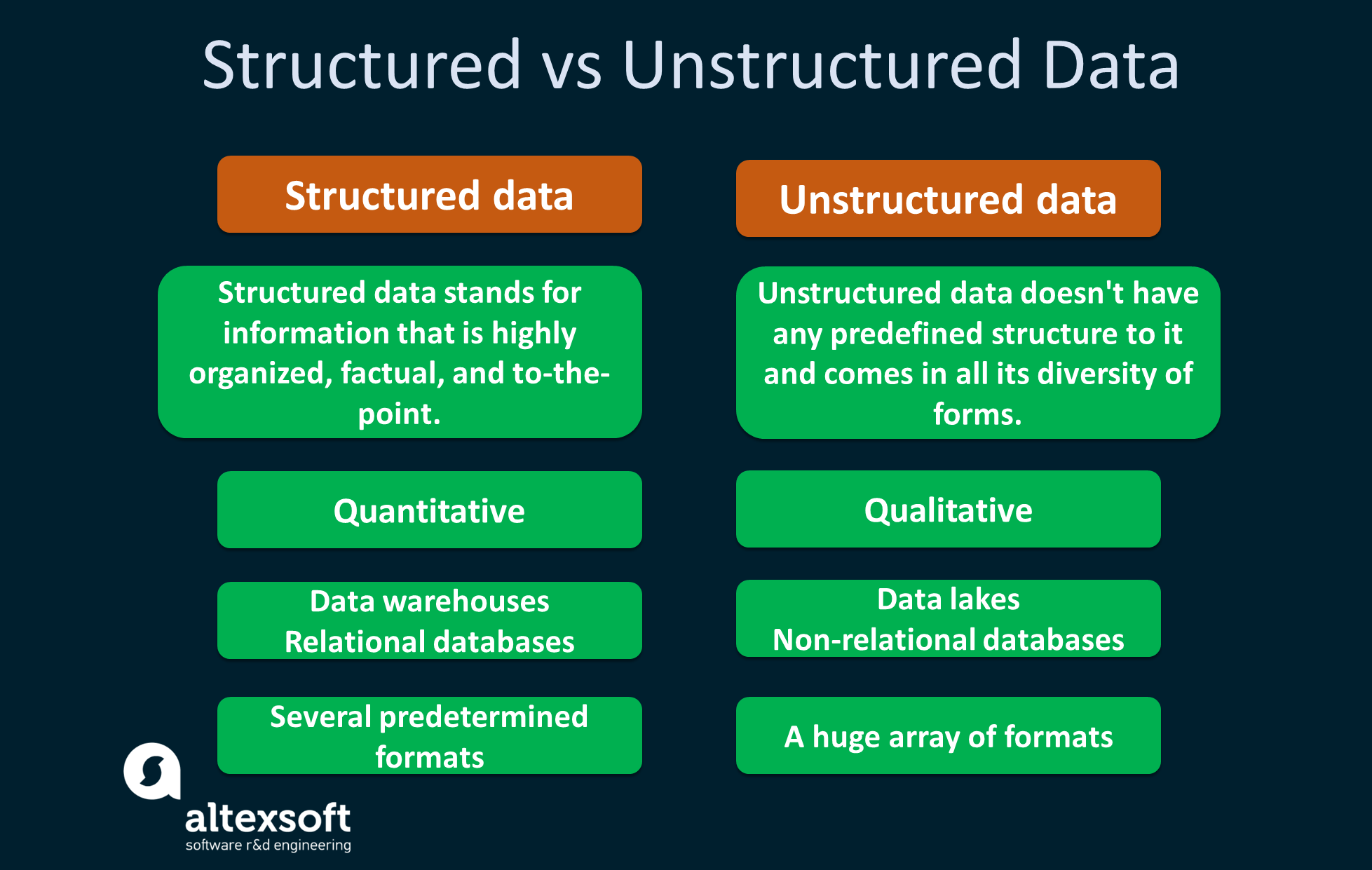
The key differences between unstructured data and structured data.
Structured data stands for information that is highly organized, factual, and to-the-bespeak. It usually comes in the form of letters and numbers that fit nicely into the rows and columns of tables. Structured data commonly exists in tables similar to Excel files and Google Docs spreadsheets.
Unstructured data doesn't accept any pre-defined construction to it and comes in all its diversity of forms. The examples of unstructured data vary from imagery and text files like PDF documents to video and sound files, to name a few.
Structured information is often spoken of as quantitative data, meaning its objective and pre-defined nature allows the states to easily count, measure, and express data in numbers. Unstructured data, alternately, is called qualitative data in the sense that information technology has a subjective and interpretive nature. This information can be categorized depending on its characteristics and traits.
With that summary, let'due south movement on to more descriptive explanations of the differences.
What is structured data?
So, structured information is the blazon of data that is well-organized and accurately formatted. This data exists in a format of relational databases (RDBMSs), meaning the information is stored in tables with rows and columns that are connected. In this way, structured information is arranged and recorded neatly, and then it can exist hands constitute and processed. As long as data fits inside the structure of RDBMSs, we can easily search for specific information and single out the relationships betwixt its pieces. Such information tin can simply exist used for its intended purpose. On top of that, structured data doesn't normally require much storage space.
For belittling purposes, y'all can apply data warehouses. DWs are central data storages used past companies for information analysis and reporting.
There is a special programming language used for handling relational databases and warehouses chosen SQL, which stands for Structured Query Language and was developed back in the 1970s by IBM.
Structured data examples. Structured data is familiar to most of the states. Google Sheets and Microsoft Function Excel files are the outset things that bound to listen apropos structured data examples. This information can comprise both text and numbers, such as employee names, contacts, Goose egg codes, addresses, credit card numbers, etc.
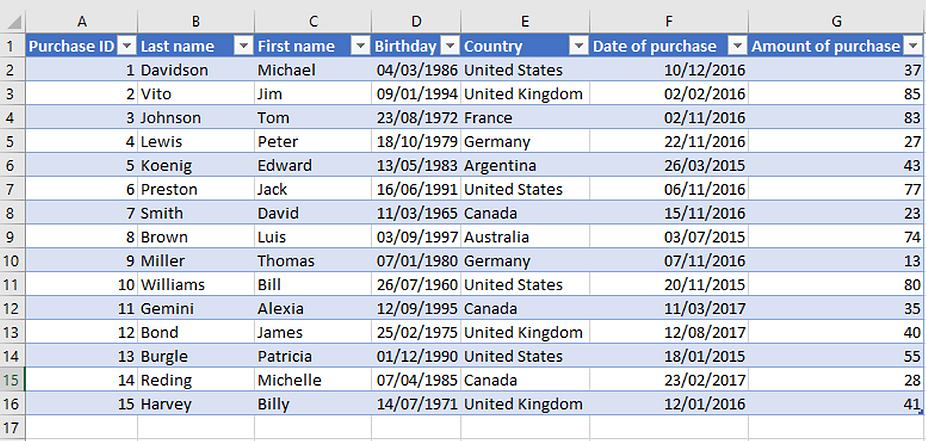 The typical structured data case: Excel spreadsheet that contains information about customers and purchases.
The typical structured data case: Excel spreadsheet that contains information about customers and purchases.
Pretty much everyone has dealt with booking a ticket via one of the airline reservation systems or withdrawing cash using an ATM. During these operations, nosotros don't ordinarily think of what kind of applications nosotros deal with and what types of data they process. However, these are the systems that typically utilize structured data and relational databases as well.
What is unstructured information?
It makes sense that if the definition of structured information implies a neat arrangement of components in a predetermined manner, the definition of unstructured data will exist the reverse. The pieces of such data aren't structured in a pre-defined way, meaning data is stored in its native formats.
The thing with unstructured information is that traditional methods and tools can't be used to analyze and process it. I of the ways to manage unstructured data is to opt for not-relational databases, as well known as NoSQL.
If at that place's a need to keep information in its raw native formats for further assay, storage repositories called data lakes volition be the way to go. A data lake is a storage repository or system meant to store huge volumes of data in its natural/raw formats.
Taking into account the whole diversity of file formats of unstructured data, it comes as no surprise that information technology makes upward more 80 percent of all data. Given this, companies ignoring unstructured data are left far behind as they don't get plenty valuable information.
Unstructured information examples. In that location is a wide array of forms that brand upwardly unstructured data such as email, text files, social media posts, video, images, sound, sensor information, and so on.
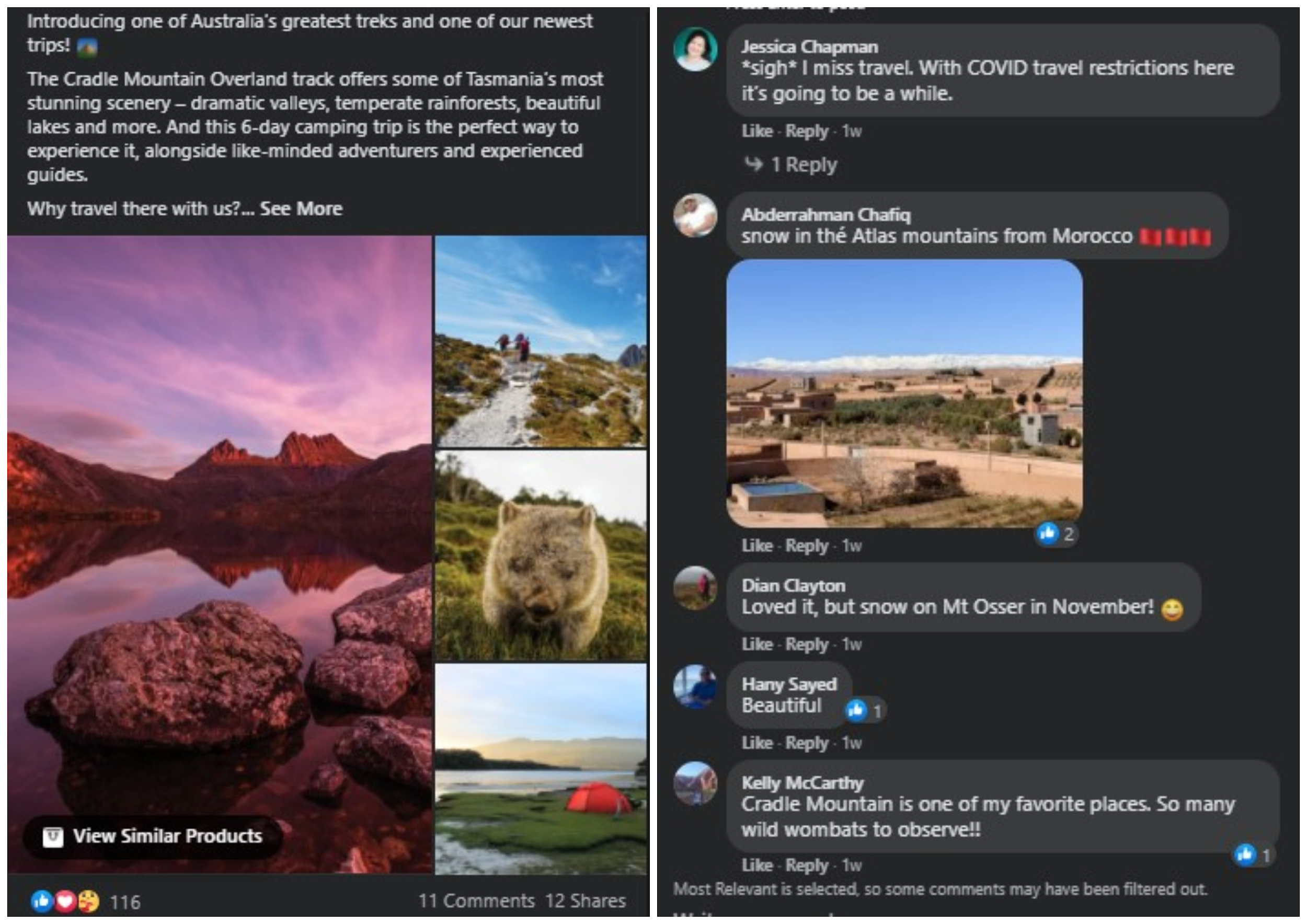
The travel bureau Facebook mail: an instance of unstructured data.
As an example, we can take social media posts of a travel agency or all posts for that affair. Each postal service contains some metrics like shares or hashtags that can be quantified and structured. Nevertheless, the posts themselves belong to the category of unstructured data. What we're trying to say hither is, information technology will accept some time, effort, cognition, and special software tools to analyze the posts and collect useful insights. If an bureau posts new travel tours and wants to know the audience's reactions (comments), they volition demand to examine the post in its native format (view the mail via social media app or use advanced techniques like sentiment analysis).
The key differences between structured and unstructured data
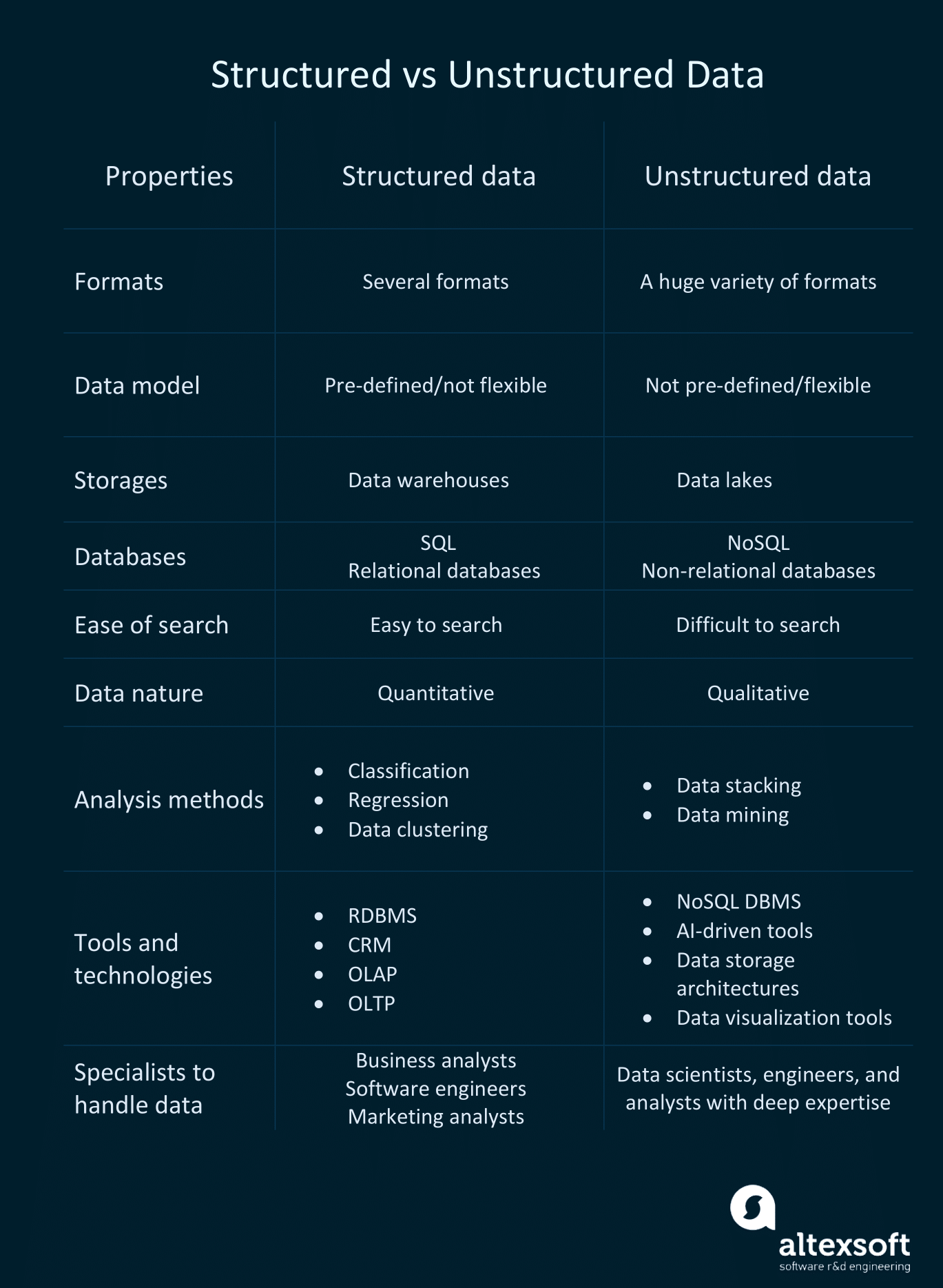
Differences between structured and unstructured data in detail.
At present let'due south discuss a few more of import differences between structured and unstructured data:
Information formats: few formats vs plethora of formats
Structured data is usually presented in the form of text and numbers. Its formats are standardized and user-readable. The most common ones are CSV and XML. In a data model, the data format has been adamant in advance.
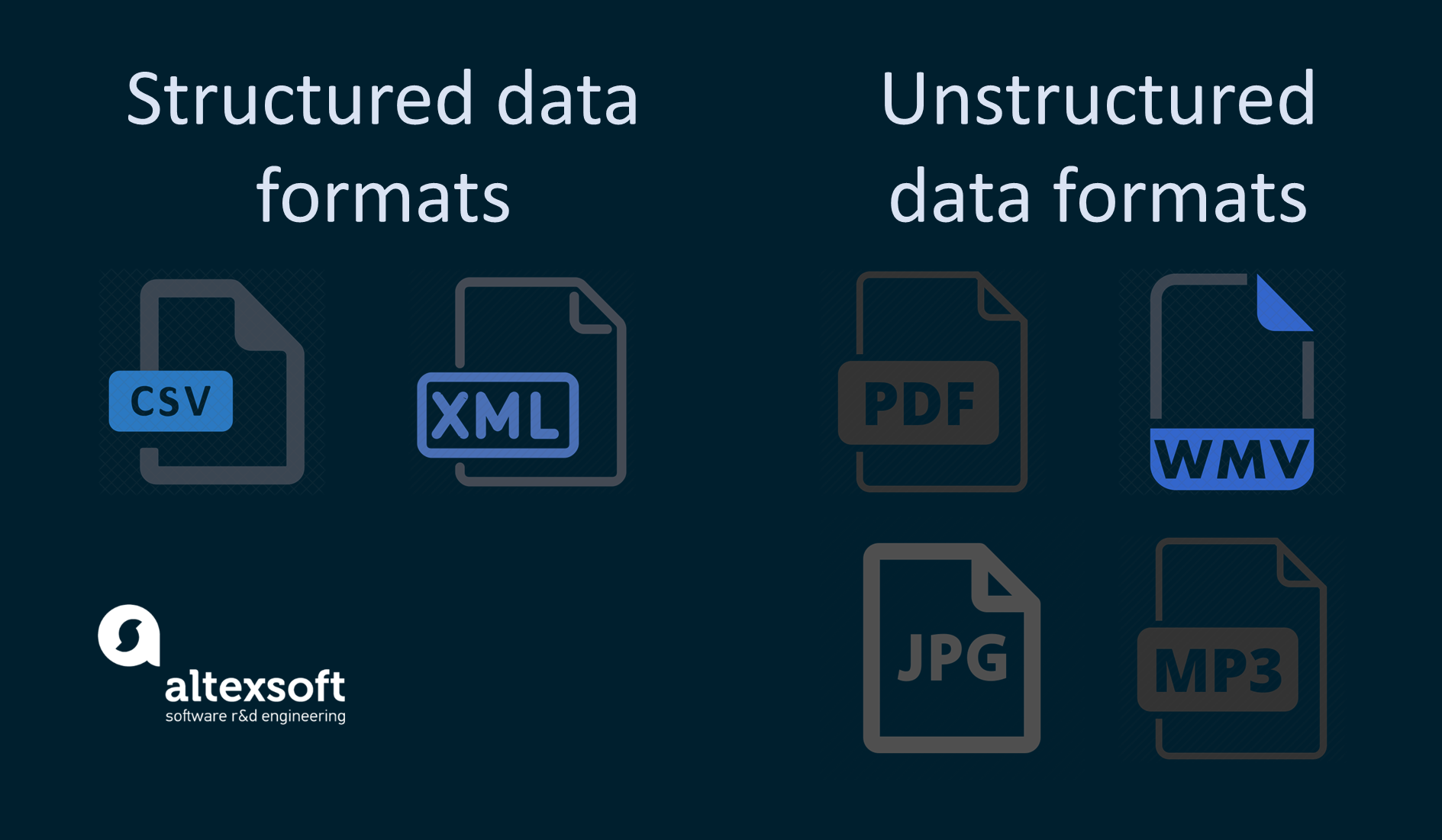
Information formats.
Unlike structured data, unstructured data formats are presented in a surfeit of different shapes and sizes. Unstructured information doesn't accept whatever pre-divers data model and it is stored in its native formats (aka "original" formats). Those tin be sound (WAV, MP3, OGG, etc.) or video files (MP4, WMV, etc.), PDF documents, images (JPEG, PNG, etc.), emails, social media posts, sensor data, etc.
Data models: pre-defined vs flexible
Structured data is less flexible every bit it relies on a strict arrangement of a data model. Such data is schema dependent. The schema of the database stands for the configuration of columns (also chosen fields) and the types of data meant to be held in these columns. Such dependency is both an advantage and a disadvantage. While the information here tin can be easily searchable and processed, all records have to follow the very strict requirements of the schema.
Unstructured data, on the other hand, offers more flexibility and scalability. The absence of the pre-divers purpose of unstructured data makes information technology super flexible every bit the data can be stored in various file formats. Notwithstanding, this data is subjective and more than difficult to piece of work with.
Storages for belittling use: data lakes vs data warehouses
If we utilise information for analytical processing and employ so-chosen information pipelines, the final destination of the structured data's journey will be special data warehouses. These are space-saving storages or repositories with a defined structure that is difficult to change. Even small-scale changes to the schema may consequence in the need to reconstruct huge volumes of information, which might entail spending time and resources.
The bigger the data volume is, the more space it requires for storage. A picture with high resolution weighs a lot more a textual file. Therefore, unstructured data requires more storage infinite and is unremarkably kept in information lakes, storage repositories that allow for storing almost limitless amounts of information in its raw formats. Apart from data lakes, unstructured data resides in native applications.
At that place is the potential for cloud-use in both cases. Not to mention that there's a new, hybrid architecture combining features of both information management systems — a data lakehouse.
Databases: SQL vs NoSQL
As we have already mentioned, structured data lives in relational databases, likewise known every bit RDBMSs. The data here is fix in tables that have a lot of rows (besides called records) and columns with labels, cogent specific data types they are supposed to go along. The configuration of data types and columns makes up the schema of the database tabular array.
Relational databases employ SQL, or Structured Query Language, to reach the stored data and manipulate it. SQL syntax is like to that of the English, providing the simplicity of writing, reading, and interpreting it.
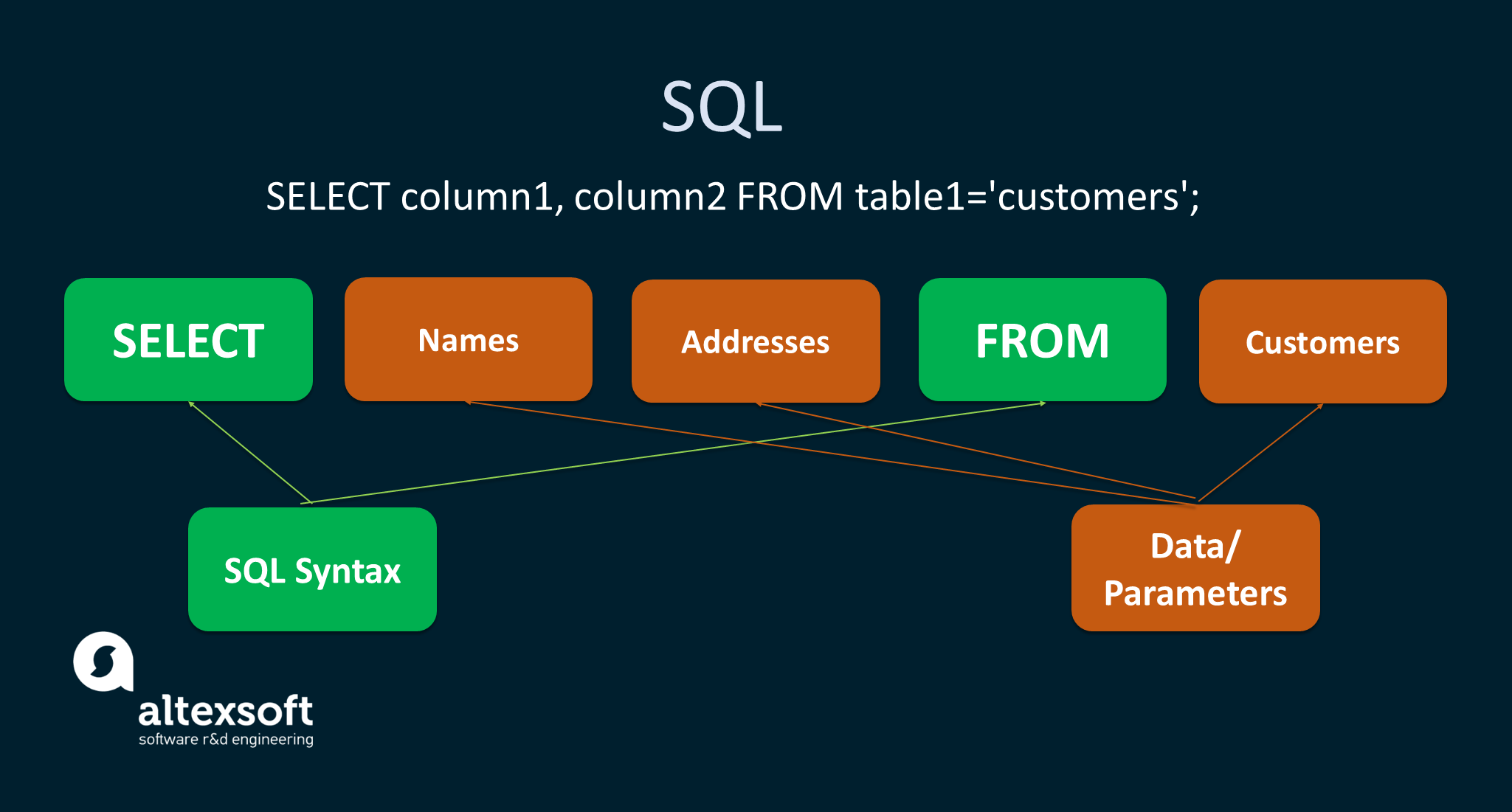 This is how SQL helps make queries.
This is how SQL helps make queries.
Speaking of databases for unstructured data, the most suitable option for this type of data volition be non-relational databases, as well known every bit NoSQL databases.
NoSQL stands for "non only SQL." These databases have diverse data models and they store data in a non-tabular fashion. The nigh common types of NoSQL databases are key-value, document, graph, and wide-cavalcade. Such databases tin process huge volumes of data and deal with high user loads as they are quite flexible and scalable. In the NoSQL world, there are collections of data rather than tables. In these collections, there are so-called documents. While the documents may look like rows in tables, they don't utilise the same schema. It'due south possible to have multiple documents in one collection that have different fields. On top of that, at that place are few to no relations between items of information. The thought here is to take less relation merging going on and instead to have super-fast and efficient queries. Although, there volition be some data duplicates.
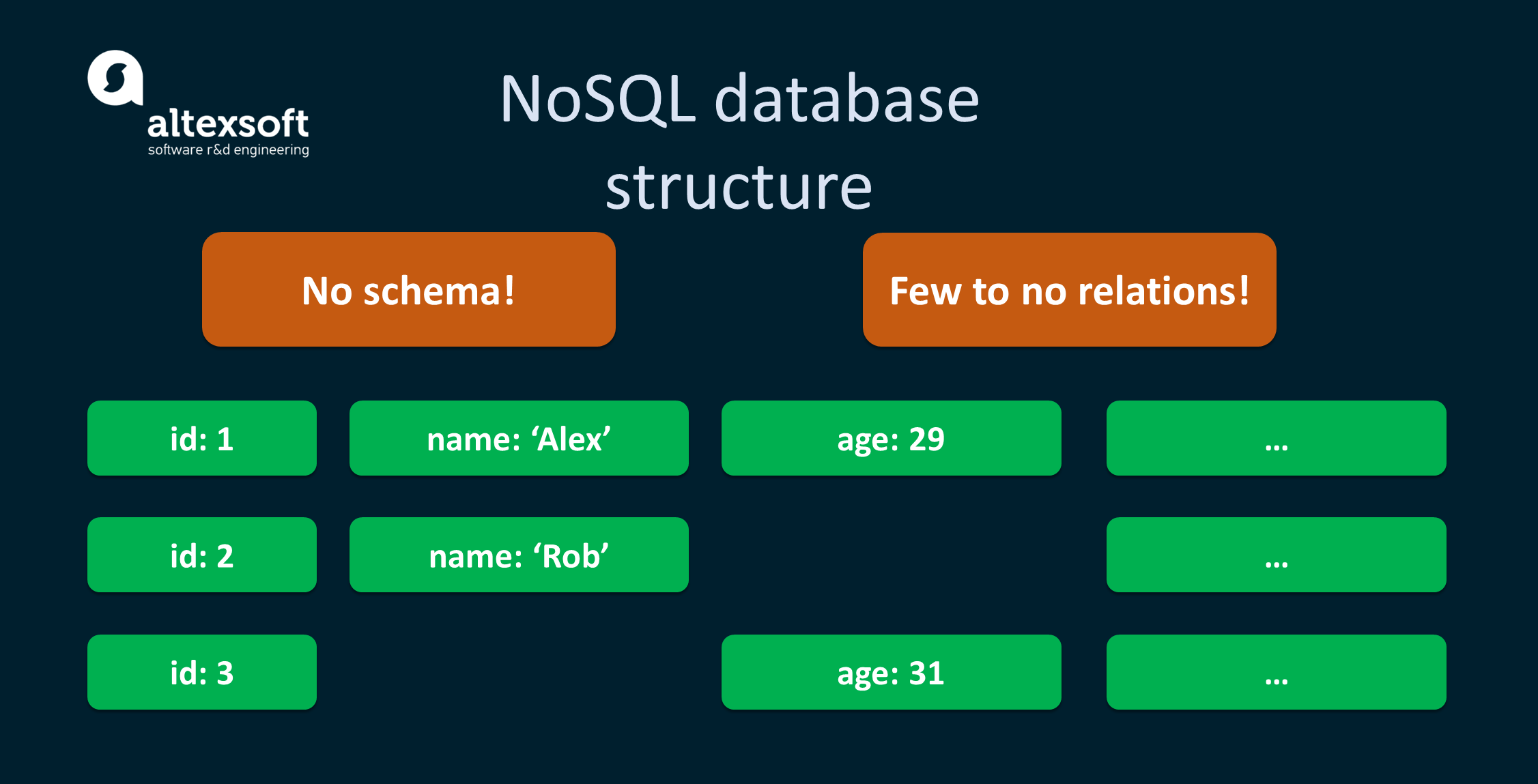
The example of a NoSQL data structure.
Ease of search, analysis, and processing
One of the main differences betwixt structured and unstructured data is how easily it can be subjected to analysis. Structured data is overall easy to search and process whether it is a man who processes data or program algorithms. Unstructured data, by contrast, is a lot more than difficult to search and analyze. Once institute, such data has to exist processed attentively to understand its worth and applicability. The process is challenging as unstructured data can't fit inside the fixed fields of relational databases until it is stacked and handled.
From a historical bespeak of view, since structured data has been here longer, it'south logical that there is a peachy choice of mature analytics tools for information technology. At the same time, those who work with unstructured information may face a poorer choice of analytics tools equally most of them are still existence developed. The usage of traditional data mining tools usually crashes into the rocks of the disorganized internal structure of this data type.
Data nature: quantitative vs qualitative
Structured information is often referred to as quantitative data. It means that such information usually contains precise numbers or textual elements that tin can exist counted. The assay methods are articulate and easy-to-apply. Among them there are:
- classification or arranging stored items of data into similar classes based on mutual features,
- regression or investigation of the relationships and dependencies between variables, and
- data clustering or organizing the data points into specific groups based on diverse attributes.
Unstructured data, in turn, is often classified as qualitative data containing subjective information that can't be handled using traditional methods and software analytics tools. For instance, qualitative data tin can menstruum from customer surveys or social media feedback in a text course. To process and analyze qualitative data, more cutting-border analytics techniques are required such as:
- data stacking or investigation of large volumes of data, splitting them into smaller items and stacking the variables with like values into a unmarried group, and
- data mining or the procedure of detecting sure patterns, oddities, and interactions in large data sets to express possible outcomes in advance.
Tools and technologies
Structured data tools. The clear-cutting and highly organized essence of structured information contributes to a wide array of information management and analytics tools. This opens opportunities for data teams in terms of picking up the near fitting software product when working with structured data.

Structured information management tools.
Amid the near commonly used relational database management systems, information tools, and technologies there are the following:
- PostgreSQL. It'due south a free, open-source RDBMS that supports both SQL and JSON querying too equally the nearly widely used programming languages such as Java, Python, C/C+, etc.
- SQLite. It's some other popular pick of an SQL database engine contained in a C library. It's a lightweight and transactional organization that doesn't rely on a separate server process every bit it is rather inserted into the end-program.
- MySQL. One of the almost popular open-source RDBMSs that is fast and reliable. It runs on a server and allows for creating both minor and large apps.
- Oracle Database. This is an advanced database management system with a multi-model structure. It tin exist used for data warehousing, online transaction processing, and mixed database workloads.
- Microsoft SQL Server. Developed by Microsoft, SQL Server is a reliable and functional relational database direction arrangement that makes it possible to store and recall data as per requests of other software applications.
- OLAP applications. A unit of business organisation intelligence (BI), online analytical processing (OLAP) stands for an advanced computing arroyo that answers multi-dimensional queries finer and swiftly. OLAP tools let users to work with data from different perspectives, because they combine data mining, a relational database, and reporting features. Apache Kylin is one of the most pop open-source OLAP systems. Information technology supports big data sets equally information technology is synced with Hadoop.
Unstructured data tools. Every bit unstructured data comes in various shapes and sizes, it requires peculiarly designed tools to exist properly analyzed and manipulated. Also, at that place'due south a necessity of finding a qualified information science team. Non only is it useful to sympathize the topic of data, simply it is as well crucial to figure out the relations of that data.

Unstructured data management tools.
Below you find a few examples of tools and technologies to manage unstructured data finer:
- MongoDB. This is a document-oriented database management system that does non require any rigid schema or structure of tables. Information technology is idea of equally ane of the classic NoSQL examples. MongoDB uses JSON-like documents.
- Amazon DynamoDB. Offered by Amazon as a part of their AWS package, DynamoBD is an advanced NoSQL database service for consummate data management. It supports certificate and key-value information structures and is a good fit for working with unstructured information.
- Apache Hadoop. This is an efficient, open-source framework used for processing large amounts of information and storing it on inexpensive article servers. Autonomously from existence a powerful tool, Hadoop is also flexible equally information technology does not require having a schema or a construction for the stored information. It helps with structuring unstructured data and then exporting this information to relational databases.
- Microsoft Azure. Presented by Microsoft, Azure is a comprehensive cloud service for edifice and managing applications and services via data centers. Azure Creation DB is a fast and scalable NoSQL database that helps with storing and analyzing masses of unstructured data.
Back in the 24-hour interval, unstructured information analysis was typically manual, and a time-consuming procedure. Nowadays at that place are quite a few advanced AI-driven tools that assist sort out unstructured information, find relevant items, and store the results. The technologies and tools for unstructured data incorporate both natural language processing and machine learning algorithms. As such, information technology is possible to accommodate software products to the needs of specific industries.
Information teams to handle data
Owing to relational databases having been here for longer, they are more familiar to a user. Data specialists with different levels of skills can work with any RDB quite easily and chop-chop as a data model is pre-defined. Any inputs, searches, queries, and manipulations are made within a highly-organized surroundings, resulting in opening self-service access to dissimilar specialists from business analysts to software engineers.
Dissimilar structured information tools, those designed for unstructured data are more complex to work with. Therefore, they require a certain level of expertise in information science and machine learning to bear deep information assay. Besides that, specialists who deal with unstructured information take to have a good understanding of a data topic and how the data is related. Given the above, to handle unstructured data, a visitor will need qualified help from data scientists, engineers, and analysts.
Structured and unstructured information examples and use cases
As we've partially touched on the subject field matter of structured and unstructured information examples above, it would be useful to point out item use cases.
And so, when yous think of dates, names, product IDs, transaction information, and so forth, you know that you have structured data in heed. At the same time, unstructured data has many faces like text files, PDF documents, social media posts, comments, images, audio/video files, and emails, to proper noun a few.
Mostly industries demand to leverage both data types to amend the efficiencies of their services.
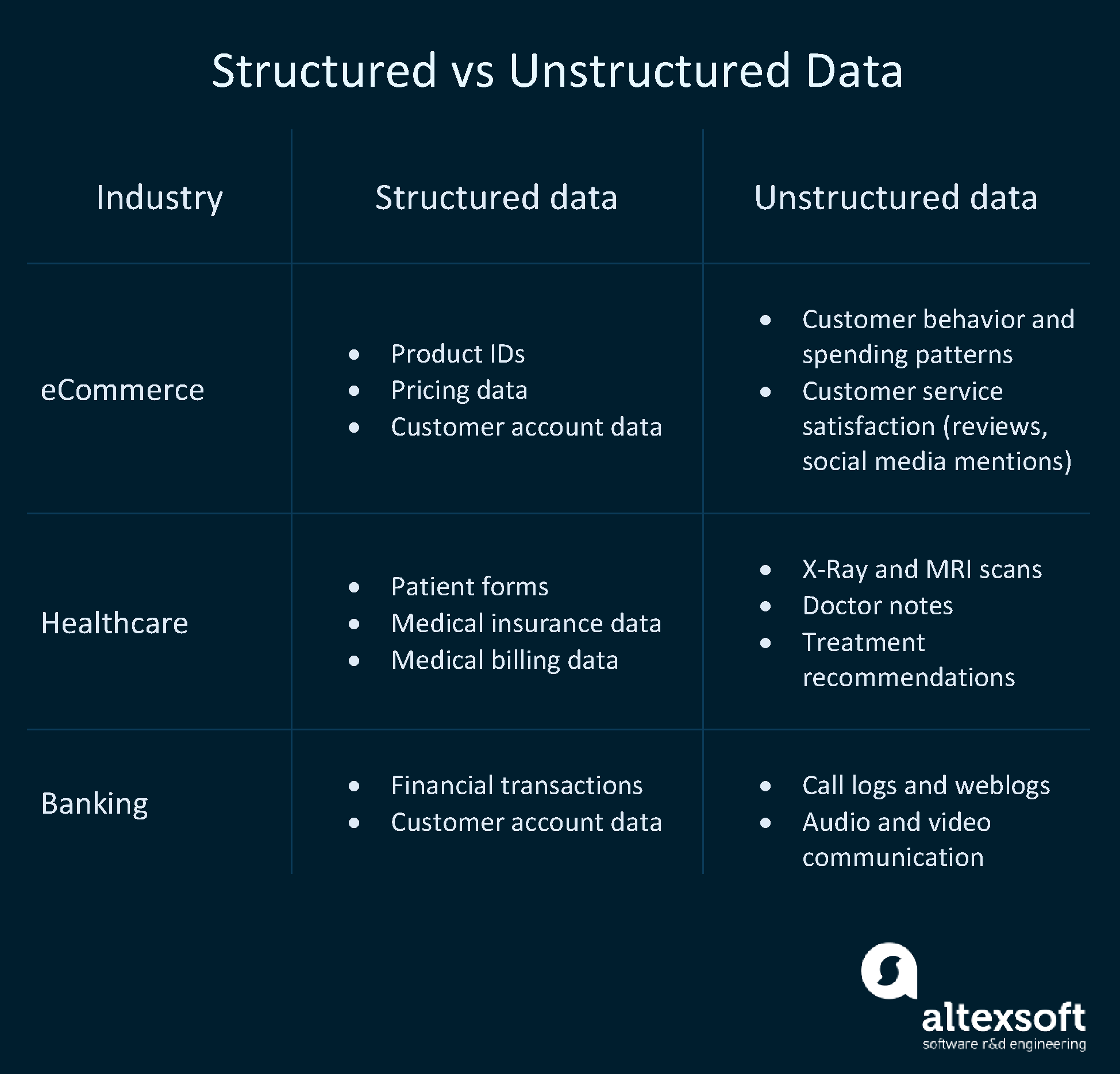
How structured and unstructured data is used in dissimilar industries.
Structured information use instance examples
Online booking. Dissimilar hotel booking and ticket reservation services leverage the advantages of the pre-divers data model as all booking information such as dates, prices, destinations, etc. fit into a standard information structure with rows and columns.
ATMs. Any ATM is a great case of how relational databases and structured data work. All the actions a user can do follow a pre-defined model.
Inventory command systems. In that location are lots of variants of inventory control systems companies use, but they all rely on a highly organized environment of relational databases.
Banking and accounting. Unlike companies and banks must process and record huge amounts of financial transactions. Consequently, they brand employ of traditional database management systems to go along structured data in place.
Unstructured information utilize instance examples
Sound recognition. Call centers employ speech recognition to identify customers and collect information virtually their queries and emotions.
Image recognition. Online retailers take advantage of image recognition and then that customers can shop from their phones by posting a photo of the desired item.
Text analytics. Manufacturers brand use of advanced text analytics to examine warranty claims from customers and dealers and elicit specific items of important information for farther clustering and processing.
Chatbots. Using natural language processing (NLP) for text analysis, chatbots help different companies heave client satisfaction from their services. Depending on the question input, customers are routed to the corresponding representatives that would provide comprehensive answers.
What is semi-structured information?
As the name suggests, semi-structured data is partially structured, meaning that information technology incorporates certain markers that can split semantic elements and implement data hierarchies, but information technology is still different from the tabular data models presented in relational databases. Such a construction is chosen self-describing. Markup languages such equally XML are the forms of semi-structured data. JSON is also a semi-structured data model that is used by new-generation databases such as MongoDB and Couchbase. There are a agglomeration of other Large Data tools and solutions that use this category of data because information technology is significantly easier to process than, say, unstructured data.

How data is organized in JSON.
Source: techEplanet
While semi-structured data may seem similar a happy medium, it is not like that. In today'due south highly competitive environs, businesses need to utilize all data sources to receive information and use it correctly to reap the benefits.
The blurred line between structured and unstructured data
Wrapping things up, information technology is worth proverb that there is no real struggle betwixt unstructured data and structured data. Both types of information carry dandy value for businesses of diverse fields and calibration. Picking a information source may depend on the structure of information. But more often than not, we don't choose i type over the other and rather look for the software opportunities to handle all data.
In the past, companies had no real way of analyzing unstructured data, so information technology was discarded while the focus was put on the information that could be easily counted. Nowadays, companies tin can utilise artificial intelligence, machine learning opportunities, and advanced analytics to do the tricky unstructured data analysis for them. For instance, corporations similar Google have made huge advances in prototype recognition technology past creating AI algorithms that can automatically detect what or who is on a photograph.
Truth be told, those lines between structured and unstructured data are a little bit blurred considering most datasets are semi-structured these days. Even if nosotros take unstructured data like a photograph, it still has components of structured data such every bit prototype size, resolution, the appointment the image was taken, etc. This information tin can be organized in a tabular format of relational databases.
Now that you know the characteristics and differences between unstructured and structured data, yous tin can brand an informed decision on whether or non you should invest in technologies to grasp unstructured data benefits. The best-case scenario for corporations is to adopt both data types, improving the effectiveness of business concern intelligence.
What Data Is Disorganized And Not Easily Read,
Source: https://www.altexsoft.com/blog/structured-unstructured-data/
Posted by: stephensexameste1969.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Data Is Disorganized And Not Easily Read"
Post a Comment